Huawei's David Wang: Driving Industry Development with F5.5G
April 29, 2022
At the 19th Huawei Global Analyst Summit (HAS), Informa Tech held the Towards F5G Evolution, Promoting Industrial Prosperity session. At this session, David Wang, Huawei Executive Director of the Board and Chairman of the ICT Infrastructure Managing Board, gave a keynote speech titled Driving Industry Development with F5.5G.
“The broadband industry has seen rapid development since the release of the F5G standard,” said Wang. “Gigabit access has become universal for homes in China and many developed countries around the world. Huawei has developed new fiber to the home (FTTH) solutions to improve the network experience of home users. In addition, Huawei’s innovative fiber to the office (FTTO) and fiber to the machine (FTTM) solutions have created many more use cases for optical networks.
Looking ahead to 2025, all industry players should work together to drive F5G evolution and satisfy home, business, and industrial needs for higher bandwidth, lower latency, and more connections. This is why we proposed F5.5G.”

(David Wang giving a keynote speech)
According to Huawei’s proposal, F5.5G will create greater value than F5G in four ways:
First, F5.5G will use next-generation technologies such as Wi-Fi 7, 50G PON, and 800G to improve home access everywhere from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps.
Second, network capabilities will move beyond telecoms level to industrial level. F5.5G will reduce network latency to microseconds, meeting the needs of industrial robot control. F5.5G will also improve network reliability from 99.99% to 99.9999%, facilitating high-frequency power grid dispatching.
Third, F5.5G will move beyond optical communication to optical sensing, which will be able to detect vibration, stress, temperature, and more through fiber scattering, and improve positioning precision to within approximately one meter.
Finally, F5.5G will boost network energy efficiency 10-fold thanks to the low energy consumption of optical technologies.
Finally, Wang called on the industry to reach a consensus on F5G evolution, and work together to shape a thriving industry ecosystem and bring network technologies to maturity.
See below for the full speech:
F5G is accelerating the development of fixed networks
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) released F5G standards in 2020, solving the problems of a fragmented broadband industry and a lack of clarity in generations. ETSI also defined the three key characteristics of F5G: enhanced fixed broadband (eFBB), full-fiber connection (FFC), and guaranteed reliable experience (GRE). The fiber broadband industry has seen accelerated and coordinated development since then.
Looking to the future, new video services such as XR, holographic projection, and naked-eye 3D will be widely applied in homes and businesses. F5G is being further integrated into electric power, high-precision manufacturing, and other major sectors, imposing higher requirements on networks. To meet all these needs, F5G must continue to evolve to drive wider adoption.

Bringing 10 Gbps everywhere with F5.5G
Huawei has proposed F5.5G as an extension of ETSI’s F5G standard to enhance F5G.
eFBB: F5.5G will use next-generation technologies such as Wi-Fi 7, 50G PON, and 800G to improve user bandwidth everywhere from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps.
FFC: F5.5G will use low-power consumption Wi-Fi technologies to connect more scenarios such as sockets, curtails, and thermometers, and use small and modular devices to deliver high-speed, secure connectivity to more industry devices. In this way, F5.5G will increase the number of connections per square kilometer from 100,000 to over one million (estimated based on simulation in Shenzhen’s Longgang District).
GRE: F5.5G will allow carriers to move beyond Level-3 autonomous driving networks to achieve Level-4 autonomy. By optimizing user data traffic and Wi-Fi coverage algorithms, home broadband networks will support both diagnosable problems and self-optimized experience. F5.5G will also improve minute-level private line service provisioning to second-level automatic path computation. In this way, F5.5G will realize fully automated home broadband and private line experience.
In addition, F5.5G will extend F5G along three dimensions.
Real-time resilient link (RRL): F5.5G will feature real-time resilient link, providing μs-level latency and 99.9999% reliability for manufacturing and other sectors.
Optical sensing & visualization (OSV): OSV will improve harmonized communication and sensing and digital operations of optical fiber, developing new use cases.
Green agile optical network (GAO): GAO will increase site energy efficiency 10-fold, consuming only 0.03 watts of power for each gigabit transmitted per site.

Wang explained how these characteristics of F5.5G will change and benefit industries.
From 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps, F5.5G will connect the real and virtual worlds
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) services are enriching people’s lives, and are beginning to be applied in some production domains. Currently, VR services require over 1 Gbps bandwidth, AR-assisted medical services require 10 Gbps bandwidth, and holographic projection for industrial design require over 1 Gbps bandwidth, which is expected to increase to 1 Tbps in the future.
With technological innovation in next-generation technologies such as Wi-Fi 7, 50G PON, and 800G, we expect that F5.5G will bring 10 Gbps everywhere for both homes and enterprises, from end-point Wi-Fi to home and enterprise access, and bandwidth transmission. F5.5G will be able to deliver up to 50 Gbps, improving user experience while maximizing the value of networks.

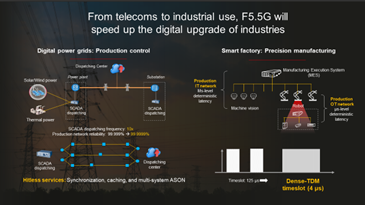
From telecoms to industrial use, F5.5G will speed up the digital upgrade of industries
In the telecoms sector, network capabilities include 50 ms protection switching, 99.99% reliability, etc. But the fact is that when F5G is applied in some industry digitalization scenarios, these telecoms-level network capabilities don’t deliver the required performance.
Take power grids, for example. On top of requiring service isolation, they also need 10 times higher SCADA dispatching frequency due to an increasing share of new energy in power generation, in order to keep service interruptions to less than 30 seconds per year and ensure stable power supply. That is to say, the target for network reliability is 99.9999%. To address these needs, we can adopt the multipath solution which is characterized by synchronization, caching, and multi-system automatically switched optical networks (ASONs).
In highly automated precision manufacturing factories, production IT networks require millisecond-level deterministic latency, while production OT networks require much less latency, even within 20 microseconds in some cases. High-density timeslot technology has changed the traditional TDM model of PON networks, reducing network latency by narrowing the timeslot interval to four microseconds. This enables millisecond-level latency from control systems to industrial robots, and reduces end-to-end jitter to less than 20 nanoseconds. F5.5G will enable fiber networks to enter core manufacturing systems and accelerate industry digitalization.
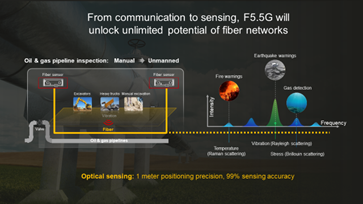
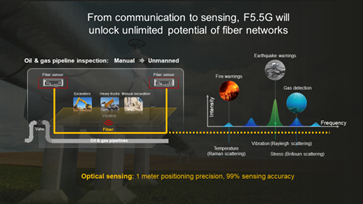
From communication to sensing, F5.5G will unlock unlimited potential of fiber networks
Research shows that fiber can be used to monitor the environment. Using Raman scattering, Brillouin scattering, and Rayleigh scattering, fiber can detect vibration, stress, temperature, etc.
In a pilot project, Huawei deployed fiber sensors as monitoring units in oil and gas pipelines. These sensors could detect vibration in areas surrounding the pipelines and use algorithms to locate construction, landslides, and other phenomena. The sensors achieved 99% event identification accuracy. In the pilot, positioning precision was accurate to within a few meters, and is expected to improve to approximately one meter. This project suggests that optical sensing and visualized management will make intelligent, unmanned oil and gas pipeline inspections a reality.
In the future, optical sensing technology will be more widely used in scenarios such as fire and earthquake warning, gas detection, and water quality inspection, as well as the digital operations of fiber networks.
F5.5G will make networks much greener with optical fiber
As a result of industry digitalization, communication networks will require 10–100 times their current capacity, and this makes it necessary to improve the energy efficiency of network technologies.
F5.5G will improve network energy efficiency in two respects. One is the transport network. Currently, a large hub optical/electrical transport node consumes over 20,000 watts of power per hour, and about 337 watts of power per Tbps. All-optical cross-connection (OXC) technology can maximize the utilization of wavelength frequency and ports, and reduce energy consumption per Tbps per site to below 32 watts. This is achieved through the combination of FlexRate, FlexGrid, FlexOSU, and FlexADN.
The other is home and campus access networks. Copper wires consume an average of about 0.03 watts of power per Tbps, even with intelligent energy saving technologies. In contrast, all-optical homes and campuses can reduce power consumption to 0.006 watts per Tbps, an 80% decrease compared to that of copper wires. This is made possible by the PON architecture, intelligent energy saving technologies, and access modes like FTTH, FTTR, FTTO, and FTTM.
F5.5G can set network construction standards for all-optical sites, homes, and campuses, making networks more energy efficient.
F5.5G: Ongoing evolution with 4 changes
F5.5G will enhance the three capabilities of F5G and extend F5G along three dimensions, bringing four major changes to industries:
First, F5.5G will use next-generation technologies such as Wi-Fi 7, 50G PON, and 800G to improve home access everywhere from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps.
Second, network capabilities will move beyond telecoms level to industrial level. F5.5G will reduce network latency to microseconds, meeting the needs of industrial robot control. F5.5G will also improve network reliability from 99.99% to 99.9999%, facilitating high-frequency power grid dispatching.
Third, F5.5G will move beyond optical communication to optical sensing, which will be able to detect vibration, stress, temperature, and more through fiber scattering, and improve positioning precision to within approximately one meter.
Finally, F5.5G will boost network energy efficiency by 10-fold thanks to the low energy consumption of optical technologies.

Huawei proposed the F5.5G concept, calling on the industry to define and reach a consensus on F5G evolution. Huawei is eager to work with industry players to create more use cases, accelerate industry digitalization, and define technology evolution pathways within the standards frameworks released by ETSI, ITU, and other standards bodies. Together, we will foster a thriving fixed network industry.
About the Author
You May Also Like












_1.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
