The implications of AI for telecomsThe implications of AI for telecoms
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will impact the global workforce, create transformational opportunities for telcos, and force the industry to review data governance frameworks.
January 29, 2024

As AI, which includes generative AI (genAI), continues to be a hotly debated topic and a key trend in 2024 for all things telecoms and tech, this article looks at the implications of AI on the telecoms industry, including its impact on workforce, intensified geopolitical tensions over chips (not the edible variety), and the opportunities the technology can unleash for telcos.
AI’s impact on the telco workforce
A recent survey conducted by telecoms.com found out that lack of skills and expertise is considered the top barrier to the widespread adoption of AI in telecoms. Indeed, there is an AI talent and skills shortage with only a small pool of AI researchers and engineers, making them highly sought after. This means closing the AI skills gap should be a key priority.
But amid continued financial pressures, layoffs in the industry have continued to grow, which risk impacting talent retention and acquisition in this space. Various players in telecoms and the tech industry, including operators and vendors, have increasingly announced job cuts which in the past two years alone have amounted to more than 150,000 job losses announced (based on data gathered by telecoms.com).
This makes balancing cost cutting with gaining new digital skills and expertise undoubtedly an important factor for telcos in their pursuit of AI. With the technology’s promise to innovate and influence product development, AI talent is becoming a hot commodity in telecoms. But the mounting layoffs could increase the challenge for both retaining existing talent and attracting new ones.
Financial pressures are not the only driver for culling jobs, with AI believed to claim its own fair share of roles. For instance when UK’s incumbent telecom operator, BT, announced cutting 40% of its workforce over a seven-year period, the operator’s departing CEO suggested that nearly 20% of the total 55,000 layoffs could be shifted to AI instead.
Those who see such developments as a glass half full argue that AI, including genAI, can complement many jobs and enhance staff productivity. In advanced economies, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) argues, three out of five jobs could be impacted by AI with about half of them indeed benefitting from AI integration.
While the IMF report does not provide a breakdown by industry, there is a lot of ongoing debate around how AI might reshape white collar jobs. For instance, in telecoms AI can enable networks to become self-sufficient or self-healing. This could reduce the need for engineers. In software development, writing lower-level codes could be replaced by genAI tools. In marketing, there is a threat to copy writing roles. These examples are not exhaustive.
Additionally, the IMF report describes how AI’s impact will go beyond immediate job effects. “As AI drives efficiency and innovations, those who own AI technologies or have stakes in AI-driven industries may experience increased capital income.”
For telcos already investing in AI or else exploring concepts of the technology, this certainly will be another sign of approval. But the key challenge for telecom operators and vendors to address may well be how best to attract AI talent and close the skills gap for existing staff. This will be especially the case as research and development (R&D) into 6G intensifies (more on 6G further below).
Opportunities and applications
Since AI is described as ‘more than just automating’ repetitive, pre-defined, or mundane tasks, many believe the applications and use cases it can unleash for telcos create multifaceted opportunities.
The intelligence aspect of the technology means it has data-driven capabilities that assist with decision-making processes, such as how to best optimise networks and predict maintenance requirements. This is believed to be true for both AI as well as its subset genAI.
For instance, using AI algorithms (and machine learning) network functions, such as network data analytics function (NWDAF), can actively monitor 5G core components and establish reporting and predictive analytics. According to Niall Norton of Amdocs, these analytics could then be used to influence the composition of 5G services and through dynamic learning anticipate network changes.
AI applications also enable operators to analyse customer usage patterns and call centre data, detect or predict faults, and make use of virtual assistants. In customer care, genAI’s natural language capabilities can enhance existing chatbots’ customer support responses beyond automated pre-defined multiple-choice options.
AI-driven network fault detection, error diagnosis, and repair features also mean telecom networks can increasingly gain self-adaptive, more zero-touch capabilities and less need for manual interventions.
Moreover, AI solution providers now offer monitoring solutions for telco network events. According to Kelvin Chaffer from Lifecycle Software, monitoring solutions that use AI algorithms can help determine crucial touch points within the customer journey and deliver pre-emptive messages best suited to the customer’s needs.
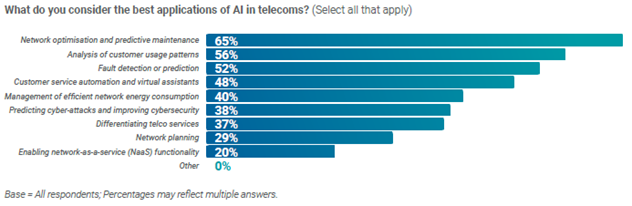
Source: Telecoms.com, Annual industry Survey 2023
These use cases and applications lead the industry to believe that AI can transform telecoms from a manual and reactive management of networks system to a more proactive and dynamic operational system.
As a result, more efficient, dynamic, and intelligent networks should then enable telcos to provide better and more differentiated services, offer faster speeds and higher network reliability, and hopefully also cut operating costs.
Risks and the business challenges to widespread adoption of AI
Another key consideration of AI in telecoms are the associated risks for organisations that plan to implement and/or share data with AI models. Given the amount of proprietary data telcos collect, it is unsurprising that security risks, including cybersecurity and data privacy breaches, are the top two associated risks for telecom professionals.
As such, it is important for the telecoms industry, including operators, vendors, software developers, and regulators, to revisit and reconsider existing data governance frameworks in the context of AI.
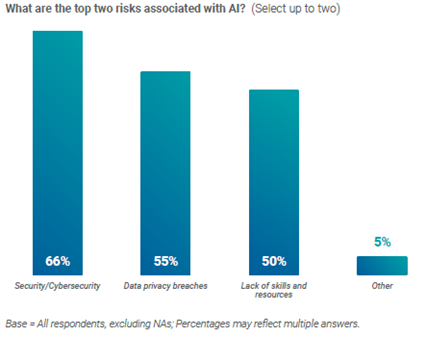
Source: Telecoms.com, Annual industry Survey 2023
But the good news is, according to industry experts such as Yannick Martel of Capgemini, there are ways for telcos to dip their toes into AI without “reckless abandonment” of associated risks.
Martel suggests Communication Service Providers (CSPs) “should take small incremental steps and test along the way. For instance, they could investigate its use across low-risk applications that enhance employee capabilities before implementing client-facing automation. CSPs should be seizing opportunities to implement small, quick changes to gain efficiencies and seek to familiarize their organization on such advancements as the technology matures.”
While resources and cybersecurity risks also act as business barriers to the widespread adoption of AI, other compelling challenges relate to unclear business cases and return on investment (ROI) as well as unclear strategies.
This indicates that those in the industry who offer AI-driven solutions still have a challenge to quantify the value AI can bring telcos and the best approaches to adoption, especially in times of financial pressures as indicated by mass layoffs discussed above.
Strategies to adoption may include collaboration with hyperscalers, who alongside their public cloud offerings also provide AI-driven tools, or existing vendor partners. Worthwhile noting that those reluctant to adopt public cloud may also be more reluctant to share their proprietary data for the use of AI.
Geopolitical tensions
As the race to AI intensifies and risks of technological monopoly in AI and other advanced technologies increase, geopolitical tensions between China and the US also continue to grow. Recent reports indicate a US initiative aiming to deprive China of access to the super-powerful chips that enable AI to run.
The US has increasingly limited access to such chips for China leaving companies in the that market with only access to degraded Nvidia chips. Meanwhile, some US-based tech giants continue to hoard AI chips unabated. Meta is expecting to have a stockpile of nearly 600,000 GPUs by the end of 2024, while Microsoft and Meta each had around 150,000 H100 Nvidia chips shipped in 2023.
What is ironic though is that the US move may have been a blunder as China has been pouring resources into its domestic semiconductor sector and now with Chinese vendor, Huawei, seemingly benefitting from the US-imposed restrictions.
It appears, in the face of these geopolitical games, Chinese companies have been turning to Huawei for their chip supplies. Despite being considered a couple of generations behind the best of breed, Huawei’s chips may still be advanced enough to keep the country in the race.
Unsurprisingly, these developments simply show that sanctions alone don’t block development and innovation. History also tells us the rivalry between the US and Russia accelerated the space race and improved R&D around space travel, so why should it be any different today with AI?
What the future holds
While AI is already being used in 4G and 5G networks to streamline operational systems, the expectation seems to be that the technology will be more heavily weaved into 6G. Perhaps in the same manner that 5G is considered cloud-native and has been designed with cloud and automation in mind, 6G is likely to be AI-native and designed with intelligent and self-adaptive capabilities, deeply integrated into its architecture.
As the AI-wave continues, the IMF also argues that its effects could exacerbate existing inequalities in our society, thus calling into question the ethics of AI, which as a topic continues to be widely discussed and reshaped.
There is a lot still on the horizon to be discovered and learned about in this topic. But one thing is clear, there will be winners and losers of AI, in business and the workforce alike, just as with any other technological advancements.
About the Author
You May Also Like





_and_Tom_Bennett_CTO_at_Freshwave_(R)_MOU.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)




.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


_1.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)