The Promise of IP + Optical Networks
June 28, 2022

According to Ian Redpath, Research Director at Omdia, the 400G Era IPoWDM has been designed a very specific cloud SP application with many design trade-offs. IP+Optical provides a more complete solution with a rich set of client side and line side options with OTN support. IP+Optical continues to deliver enduring value for CSPs. For detailed comparative analyses about IPoWDM and IP+Optical, please see the white paper: https://omdia.tech.informa.com/commissioned-research/articles/ip-optical-networks
Communications service providers (CSPs) are investigating IP over WDM (IPoWDM), attracted by its purported network simplification and economic improvements. However, CSPs’ network and operational requirements are far more complex than that of a cloud service provider (cloud SP) niche.
CSPs contend with the following:
ROADM-rich networks; wavelengths must pass through many ROADMs
A need to support a multitude of client-side speeds: 10G, 25G, 50G, 100G, and FlexE
A desire to support maximum line speeds per distance, leveraging multiple modulation formats
Transitioning to an IPoWDM is a tremendous integration and operational effort, explained as follows:
The standards for multi-layer, multi-vendor operations are not mature
CSPs must be aware of a huge integration effort and cost for multi-layer or multi-vendor control
IP + optical continues to demonstrate enduring value for the CSP community in the following areas:
“The cheapest transponder is no transponder.” CSPs will continue to leverage optical bypass
Major advances in wavelength management in the network core and at the edge
CSPs desire to maximise spectral efficiency and total system capacity
Introducing L0-L3 network architectures
The IPoWDM concept has been around for many years, offering the ability to deploy transmission optics within routing platforms to delayer and simplify networks. Cloud SPs have latched on to IPoWDM for a very specific point-to-point (P2P), short-reach need in their networks.
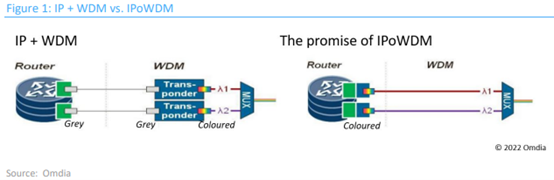
CSPs have picked up on the IPoWDM concept, attracted by its purported network simplification and economic improvements. However, CSPs’ network and operational requirements are far more complex than that of a niche within the cloud SP community. The communications industry has become slightly torn by the allure of IPoWDM, which will succeed in a very narrow, designed-for niche, but remain untenable for many CSP networks and applications.
CSP challenges and network layer integration
In contrast to the cloud SP niche (where IPoWDM may work for some cloud SPs), CSPs have more complex network needs. CSP optical network requirements include the following:
Multiple system reach requirements from DCI, metro, national, and subsea
Many CSP networks are ROADM-rich, meaning wavelengths must pass through many ROADMs
A desire to maximise spectral efficiency
A desire to maximise total system capacity
A need to support a multitude of client side speeds: legacy sub-rates, 1G, 10G, 25G, 50G, 100G, and FlexE
A desire to support maximum line speeds per distance, leveraging programmable modulation formats for traditional and specialised line speeds: 200G, 400G, 600G, and 800G and 150G, 300G, and 500G
The devil in the IPoWDM details
CSPs were attracted to the network delayering and purported TCO savings enabled by IPoWDM.
However, once A CSP’s network needs and requirements are factored, the promise of IPoWDM falls apart, leaving CSPs with a multi-variant problem: for IPoWDM to work, very small form-factor
pluggables are required. However, to get the pluggables down to QSFP-DD size, key capabilities and performance are sacrificed. To meet CSPs’ true network needs, the form factor size and power draw must increase, but if this happens, the optics can no longer pair with the router host paradigm.
The IPoWDM concept has been around for almost two decades but has never taken off because of challenges around optimising application performance, power draw, and form factor size. Historically, optics have been too large and consumed too much power, thus devaluing the router’s core capabilities.
The challenge continues to this day, as shown in Figure 2.

CSP networks have distinct needs from cloud data center interconnect (DCI) applications, for which space and power must be preserved and functional integration has a high value. In CSP networks, however, the equation changes in that scale is imperative; optical systems must be massively scalable. IP functionality is optimally delivered with best-of-breed routing capabilities, not muddied by non-core functions.
While a very high degree of convergence and integration is desirable for DCI applications, convergence in CSP networks would lead to performance penalties.
IPoWDM demonstrates a similar dynamic in that integration will be valuable in selected network niches, such as its initial design for very short-reach DCI applications. Yet, IPoWDM has turned out to be restrictive in CSP network situations where best-of-breed, functional specialisation, and scale are design imperatives.
IPoWDM claimed to bring great network economic benefits but has fallen short for the CSP community.
The following purported common equipment savings have not materialised:
The “cage” for a pluggable will see costs in both a dedicated optical platform and a router
IPoWDM architectures are low cost in only short-reach P2P scenarios
Grey optics are scaled and continue to see rapidly reduced costs
IPoWDM introduces a step function management and control cost
IP + optics continues to demonstrate enduring value for the CSP community in the following areas:
“The cheapest transponder is no transponder.” CSPs will continue to leverage optical bypass
Major advances in wavelength management continue, both in the core, at scale, and at the edge
CSPs can continue to quickly leverage best-of-breed technology developments
Meets CSPs’ desire to maximise spectral efficiency
Meets CSPs’ desire to maximise total system capacity
IPoWDM has begun in a unique market niche, with many design trade-offs at play. For CSPs, the promise of IPoWDM results in disappointment because IPoWDM will not meet the bulk of CSP network requirements. CSPs may deploy IPoWDM in niche situations but scale belongs to IP + WDM and mature and functional ecosystems.
About the Author
You May Also Like










.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


_1.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)