Where 5G and 5.5G Will Create Big Value (Tech Strategy – Daily Article)
October 19, 2023

We’re about 4 years into the deployment of 5G. And we now know what use cases make sense for 5G in practice. It’s not the speculation it used to be. We know the use cases that are getting traction.
But Huawei is now rolling out 5.5G (also called 5G Advanced or 5G-A). This is a 10x improvement in speed over 5G. And we’re now getting some early looks at use cases for 5.5G. Overall, it looks like it is going to be another big year in digital infrastructure.
Five Scenarios Where 5G and 5.5G Create Big Value
I was recently in Dubai for the Mobile Broadband Forum. That’s a +14-year-old annual event that provides a good look at the latest in mobile infrastructure. It tends to be a good place to see case studies on what mobile carriers are doing around the world.
At the Dubai conference, Cao Ming (Huawei President of Wireless Solutions) announced the launch of a full series of solutions for implementing 5.5G. Basically everything a carrier would need to upgrade. For those interested in the technical side, this includes:
An extremely large antenna array (ELAA) that boosts a commercial 5G network’s TDD coverage and energy efficiency.
A mm Wave AAU with +2,000 antenna elements to overcome the limitations of mm Wave.
DIS improvements in performance and energy (so 5.5G works indoors).
Huawei’s Li Peng (President of Carrier Business Group) laid out a pretty clear summary of where 5G and 5.5G are going to create large value.

The 5 scenarios for 5G and 5.5G are:
Glasses Free 3D
Self-Guided Vehicles
Next Gen Manufacturing
Cellular IoT
Intelligent Computing Everywhere
Scenario 1: Glasses Free 3D (Which Is Really Cool)
3D without glasses is using super-fast connectivity to do real-time rendering of 2D video with generative AI. You stream a video from your smartphone (which is 2D video), which is then converted to 3D in the cloud by generative AI, which is then streamed to a device for viewing in 3D. It can be viewed on a smartphone, laptop, or tablet. And you can watch without glasses and see it is 3D (somewhat). It’s pretty cool. Here’s what it looks like.


But the great example which convinced me of glasses free 3D is complete 3D-to-3D video. This is when the video is filmed in 3D and then projected on special computers (see below). This basically creates a holograph that you can view from almost any angle. In the below example, you can look at all sides of the projected car. It’s fantastic. I’m buying one of these as soon as they are available.
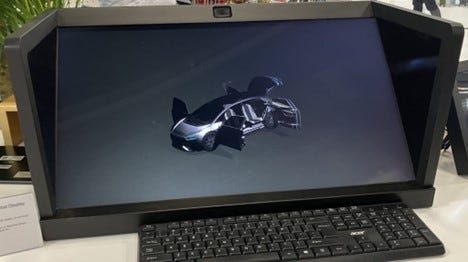
Glasses free 3D is a good use case for 5G and 5.5G. And 3D virtual humans are on the way. As well as XR.
Scenario 2: Self-Guided Vehicles
Transportation and self-guided vehicles have always been a big part of the 5G story. They require low latency (moving vehicles can’t have lags). And the amount of data required to safely control a car or vehicle is huge. They also require high reliability. As will be discussed in the next article, South Korea (a 5G leader) is really focused on this particular use case.
So 5G and 5.5G is about increasing the data to vehicles by 100x and making them intelligent. Vehicle-to-cloud collaboration is what gets you self-driving cars. Also, self-driving buses and other transportation vehicles.
However, they you start thinking about vehicle-to-vehicle communication and collaboration. And then vehicle-to-road communication and collaboration. Think millions of vehicles are communicating with intelligent traffic lights and road cameras. Which quickly becomes a discussion about smart cities and urban environments.

Here’s a slide from Li Peng on this. Note the data requirements.
Scenario 3: Next Generation Manufacturing. The Key to Enterprise Transformation.
This is the scenario I am most excited about.
First, you create a private 5G network for a manufacturer or other business. You put sensors everywhere. You start to gather tons of data. And then you connect it to the cloud and lots of digital and AI capabilities start to get applied. The result is:
The enterprise becomessmart and data driven. IoT is a massive increase in data collected and analyzed in a business. Everything is increasingly running through AI and other cloud-based capabilities.
Operations becomeautomated. Decisions start to happen without people in the loop. Certain workflows happen and adjust automatically. At the speed of algorithms.
But then something else happens.
Production becomes flexible and dynamic. Think about a typical auto manufacturing facility that needs to adjust its 10-20 production lines each year. In a digitized factory, the adjustment time can drop from weeks to days. Utilization increases, which saves money. But it also starts to become more responsive to changes in demand, so revenue can increase. Increasingly, we are even seeing parts of factories self-organize and assemble into different configurations.
Production starts to directly interact with demand. So, there is lots of data flowing between customers and production. But a flexible production system can start to make different things on demand. It can also personalize to individual users or user groups. Basically, the interactions with customers start to become two directional. Not only can production increasingly predict and personalize to demand. It can also increasingly shape demand. IoT stops being about efficiency and cost savings. And becomes more about revenue generation and creating demand.

Scenario 4: Cellular IoT
This is another scenario I think is transformative. Think data streams connecting billions of devices everywhere, using cellular networks. Suddenly everything is connected to everything.
To achieve this, you need cellular IoT. And you need a range of IoT devices and capabilities.
Passive IoT is cheap and pretty easy to place everywhere. Think about little stickers you can put on every parcel in a truck. It’s cheap but it is also very limited in capabilities.
For real IoT and for what was described in Scenario 3, you want real-time cameras and other sensors with greater connectivity. But that creates cost problems when you have to deploy thousands of them. This is especially a problem for SMEs.
Here is the range of IoT capabilities you probably need.
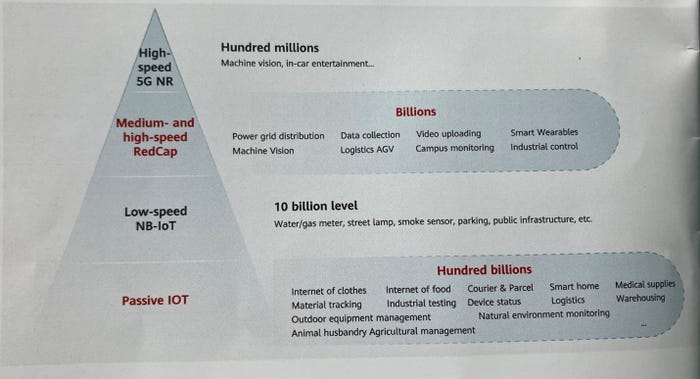

One of the cool things about 5.5G is its remote sensing capability (which 5G doesn’t have). Huawei has also been advocating “reduced capability” sensors in China (called Red Cap). Passive IoT is more powerful than RedCap. But also, cheaper than larger sensors. There are about 50 types of these devices and they have already been deploying in China. They are taking Red Cap international this year.
Last Scenario: Intelligent Computing Everywhere
A 10x increase in network capability is coming. Networks are becoming natively intelligent. And you just plug into intelligence like plugging into electricity through an outlet. Although intelligence will be running through the walls and the air. And the air interface looks like it will be dominant.

About the Author
You May Also Like


.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)







.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


_1.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)